license: mit
language: multilingual
library_name: torch
tags: []
base_model: BAAI/bge-m3
datasets:
- philipp-zettl/GGU-xx
- philipp-zettl/sentiment
metrics:
- accuracy
- precision
- recall
- f1-score
model_name: Multi-Head Sequence Classification Model
pipeline_tag: text-classification
widget:
- text: Hello, how are you?
label: '[GGU] Greeting'
- text: Thank you for your help
label: '[GGU] Gratitude'
- text: Hallo, wie geht es dir?
label: '[GGU] Greeting (de)'
- text: Danke dir.
label: '[GGU] Gratitude (de)'
- text: I am not sure what you mean
label: '[GGU] Other'
- text: Generate me an image of a dog!
label: '[GGU] Other'
- text: What is the weather like today?
label: '[GGU] Other'
- text: Wie ist das Wetter heute?
label: '[GGU] Other (de)'
Multi-Head Sequence Classification Model
Model description
The model is a simple sequence classification model based on hidden output layers of a pre-trained transformer model. Multiple heads are added to the output of the backbone to classify the input sequence.
Model architecture
The model is a simple sequence classification model based on hidden output layers of a pre-trained transformer model.
The backbone of the model is BAAI/bge-m3 with 1024 output dimensions.
An additional layer of (GGU: 3, sentiment: 3) is added to the output of the backbone to classify the input sequence.
You can find a mapping for the labels here:
GGU
- 0: Greeting
- 1: Gratitude
- 2: Other
sentiment
- 0: Positive
- 1: Negative
- 2: Neutral
The joint architecture was trained using the provided implementation (in repository) of MultiHeadClassificationTrainer.
Use cases
Use cases: text classification, sentiment analysis.
Model Inference
Inference code:
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
from .model import MultiHeadSequenceClassificationModel
import torch
model = MultiHeadSequenceClassificationModel.from_pretrained('philipp-zettl/multi-head-sequence-classification-model')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('BAAI/bge-m3')
def predict(text):
inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True)
outputs = model(**inputs)
return outputs
Model Training
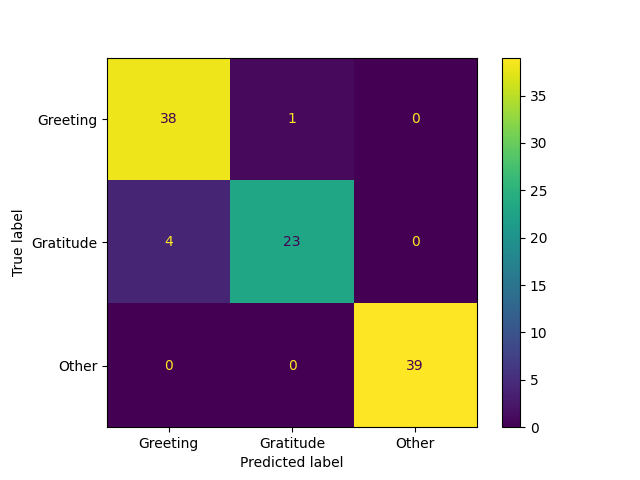
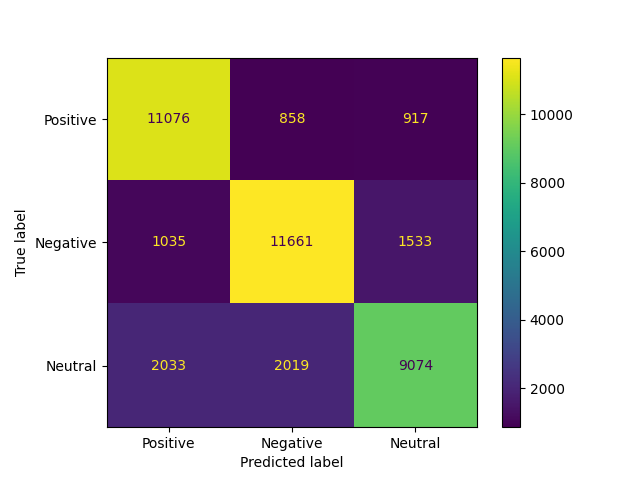
Confusion Matrix
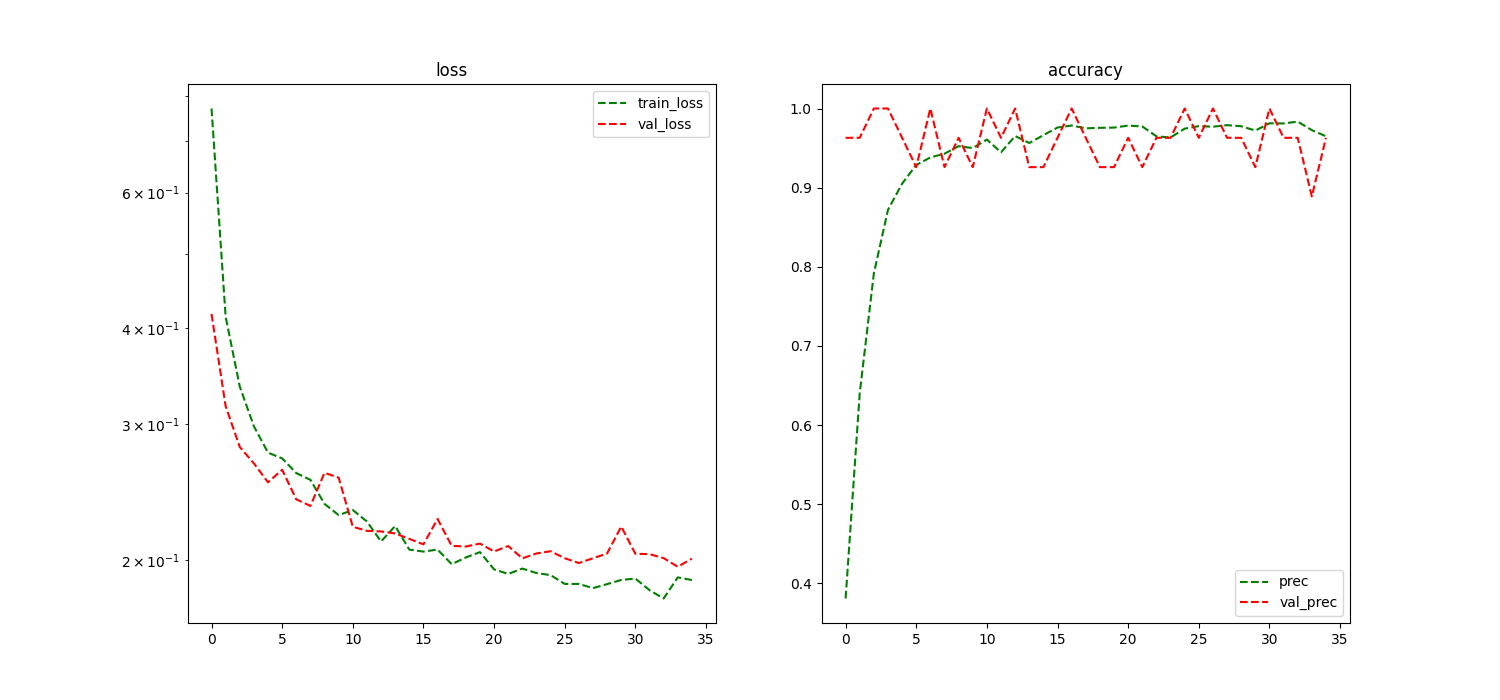
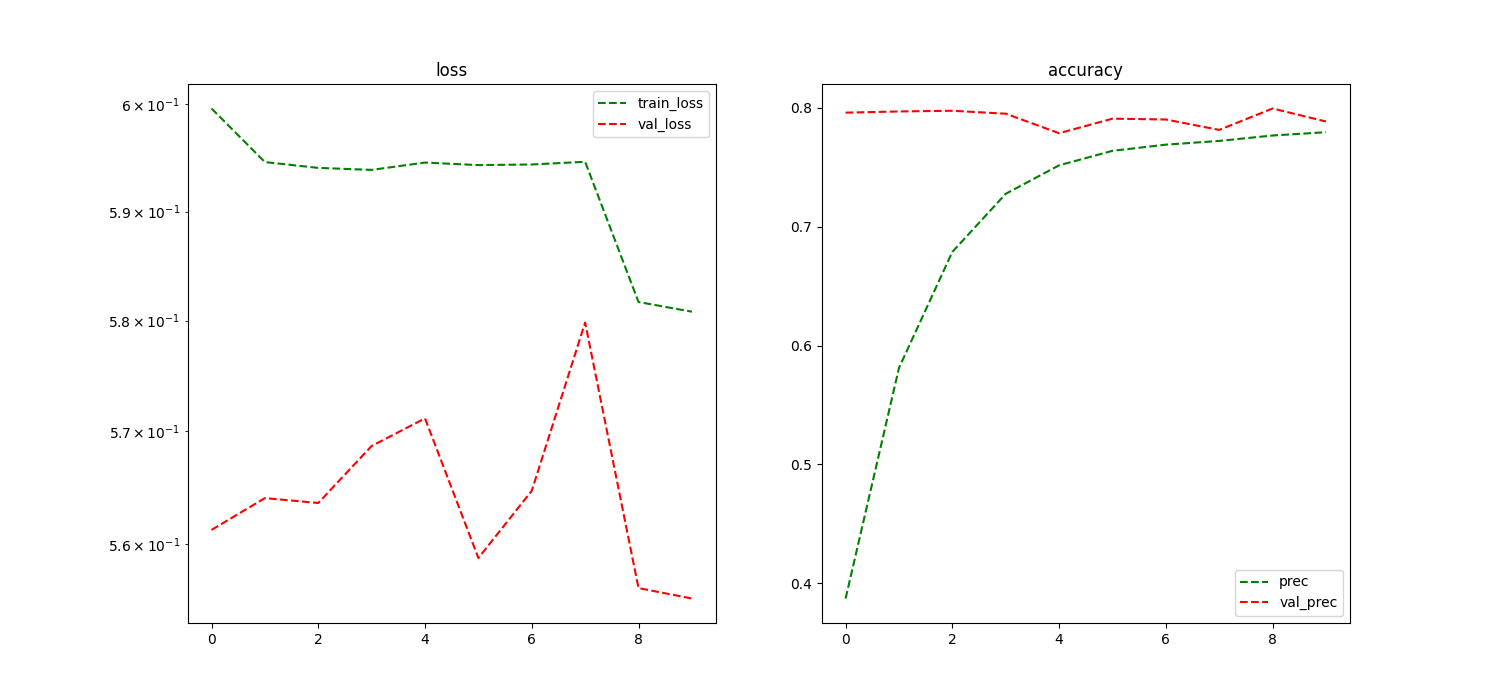
Training Loss
Training data
The model has been trained on the following datasets:
Using the implementation provided by MultiHeadClassificationTrainer
Training procedure
The following code has been executed to train the model:
def train_classifier():
backbone = AutoModel.from_pretrained('BAAI/bge-m3').to(torch.float16)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('BAAI/bge-m3')
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
ggu_label_map = {
0: 'Greeting',
1: 'Gratitude',
2: 'Other'
}
sentiment_label_map = {
0: 'Positive',
1: 'Negative',
2: 'Neutral'
}
num_labels = len(ggu_label_map.keys())
# HParams
dropout = 0.25
learning_rate = 3e-5
momentum = 0.9
l2_reg = 0.25
l2_loss_weight = 0.25
model_conf = {
'backbone': backbone,
'head_config': {
'GGU': num_labels,
},
'dropout': dropout,
'l2_reg': l2_reg,
}
optimizer_conf = {
'lr': learning_rate,
'momentum': momentum
}
scheduler_conf = {
'factor': 0.2,
'patience': 3,
'min_lr': 1e-8
}
train_run = 1000
trainer = MultiHeadClassificationTrainer(
model_conf=model_conf,
optimizer_conf={**optimizer_conf, 'lr': 1e-4},
scheduler_conf=scheduler_conf,
num_epochs=35,
l2_loss_weight=l2_loss_weight,
use_lr_scheduler=True,
train_run=train_run,
auto_find_batch_size=False
)
new_model, history = trainer.train(dataset_name='philipp-zettl/GGU-xx', target_heads=['GGU'])
metrics = history['metrics']
history['loss_plot'] = trainer._plot_history(**metrics)
res = trainer.eval({'GGU': ggu_label_map})
history['evaluation'] = res['GGU']
total_history = {
'GGU': deepcopy(history),
}
trainer.classifier.add_head('sentiment', 3)
trainer.auto_find_batch_size = False
new_model, history = trainer.train(dataset_name='philipp-zettl/sentiment', target_heads=['sentiment'], sample_key='text', num_epochs=10, lr=1e-4)
metrics = history['metrics']
history['loss_plot'] = trainer._plot_history(**metrics)
res = trainer.eval({'sentiment': sentiment_label_map}, sample_key='text')
history['evaluation'] = res['sentiment']
total_history['sentiment'] = deepcopy(history)
label_maps = {
'GGU': ggu_label_map,
'sentiment': sentiment_label_map,
}
return new_model, total_history, trainer, label_maps
Evaluation
Evaluation data
For model evaluation, a 20% validation split was used from the training data.
Evaluation procedure
The model was evaluated using the eval method provided by the MultiHeadClassificationTrainer class:
def _eval_model(self, dataloader, label_map, sample_key, label_key):
self.classifier.train(False)
eval_heads = list(label_map.keys())
y_pred = {h: [] for h in eval_heads}
y_test = {h: [] for h in eval_heads}
for sample in tqdm(dataloader, total=len(dataloader), desc='Evaluating model...'):
labels = {name: sample[label_key] for name in eval_heads}
embeddings = BatchEncoding({k: torch.stack(v, dim=1).to(self.device) for k, v in sample.items() if k not in [label_key, sample_key]})
output = self.classifier(embeddings.to('cuda'), head_names=eval_heads)
for head in eval_heads:
y_pred[head].extend(output[head].argmax(dim=1).cpu())
y_test[head].extend(labels[head])
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
accuracies = {h: accuracy_score(y_test[h], y_pred[h]) for h in eval_heads}
f1_scores = {h: f1_score(y_test[h], y_pred[h], average="macro") for h in eval_heads}
recalls = {h: recall_score(y_test[h], y_pred[h], average='macro') for h in eval_heads}
report = {}
for head in eval_heads:
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test[head], y_pred[head], labels=list(label_map[head].keys()))
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm, display_labels=list(label_map[head].values()))
clf_report = classification_report(
y_test[head], y_pred[head], output_dict=True, target_names=list(label_map[head].values())
)
del clf_report["accuracy"]
clf_report = pd.DataFrame(clf_report).T.reset_index()
report[head] = dict(
clf_report=clf_report, confusion_matrix=disp, metrics={'accuracy': accuracies[head], 'f1': f1_scores[head], 'recall': recalls[head]}
)
return report
Metrics
For evaluation, we used the following metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score. You can find a detailed classification report here:
GGU:
| index | precision | recall | f1-score | support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Greeting | 0.904762 | 0.974359 | 0.938272 | 39 |
| 1 | Gratitude | 0.958333 | 0.851852 | 0.901961 | 27 |
| 2 | Other | 1 | 1 | 1 | 39 |
| 3 | macro avg | 0.954365 | 0.94207 | 0.946744 | 105 |
| 4 | weighted avg | 0.953912 | 0.952381 | 0.951862 | 105 |
sentiment:
| index | precision | recall | f1-score | support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Positive | 0.783088 | 0.861878 | 0.820596 | 12851 |
| 1 | Negative | 0.802105 | 0.819524 | 0.810721 | 14229 |
| 2 | Neutral | 0.7874 | 0.6913 | 0.736227 | 13126 |
| 3 | macro avg | 0.790864 | 0.790901 | 0.789181 | 40206 |
| 4 | weighted avg | 0.791226 | 0.7912 | 0.789557 | 40206 |